Abstract:
Not long after the advent of The Internet, the creation of worms, viruses, and other malware had become prevalent. Microsoft based platforms were the original serious target, because of poor security measures. Over time, malware had started to attack Linux based Android mobile phones. Now, the latest attacks appear to be hitting Linux based consumer grade internet routers, which were originally used to help protect Microsoft Windows based platforms in the home. These attacks have spiked in the first two months of 2014.
2013-01-11 - How I saved your a** from the ZynOS (rom-0) attack!! (Full disclosure)
2014-02-14 - Bizarre attack infects Linksys routers with self-replicating malware
2014-02-17 - Dear Asus router user: You’ve been pwned, thanks to easily exploited flaw
Conclusions:
If you are doing any serious internet based work, one might suggest that care is taken to watch the firmware of your consumer grade internet router, and upgrade the firmware as they become available. If you are running a business, a commercial grade router with a managed service may be of special interest. A short PDF on "SOHO Pharming" helps clarify risks. The avoidance of Linux based Android phones or consumer grade Linux routers may be the next best step.
 |
| [Huawei TP-Link image, courtesy rootatnasro] |
Hello everyone, I just wanted to discuss some vulnerability I found and exploited for GOODNESS .. just so that SCRIPT KIDIES won’t attack your home/business network .
Well, in Algeria the main ISP ( Algerie Telecom ) provide you with a router when you pay for an internet plan. So you can conclude that every subscriber is using that router . TD-W8951ND is one of them, I did some ip scanning and I found that every router is using ZYXEL embedded firmware.
 |
| [Linksys Router, courtesy ARS Technica] |
Linksys is aware of the malware called “The Moon” that has affected select older Linksys E-Series routers and select older Wireless-N access points and routers. The exploit to bypass the admin authentication used by the worm only works when the Remote Management Access feature is enabled. Linksys ships these products with the Remote Management Access feature turned off by default. Customers who have not enabled the Remote Management Access feature are not susceptible to this specific malware. Customers who have enabled the Remote Management Access feature can prevent further vulnerability to their network, by disabling the Remote Management Access feature and rebooting their router to remove the installed malware. Linksys will be working on the affected products with a firmware fix that is planned to be posted on our website in the coming weeks.
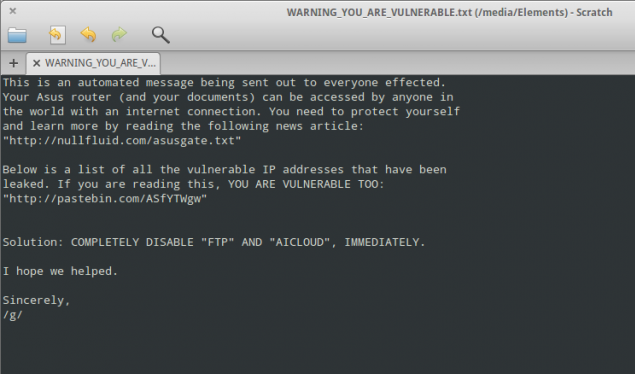 |
| [ASUS Warning, courtesy ARS Technica] |
"This is an automated message being sent out to everyone effected [sic]," the message, uploaded to his device without any login credentials, read. "Your Asus router (and your documents) can be accessed by anyone in the world with an Internet connection. You need to protect yourself and learn more by reading the following news article: http://nullfluid.com/asusgate.txt."
...
Two weeks ago, a group posted almost 13,000 IP addresses its members said hosted similarly vulnerable Asus routers.
Conclusions:
If you are doing any serious internet based work, one might suggest that care is taken to watch the firmware of your consumer grade internet router, and upgrade the firmware as they become available. If you are running a business, a commercial grade router with a managed service may be of special interest. A short PDF on "SOHO Pharming" helps clarify risks. The avoidance of Linux based Android phones or consumer grade Linux routers may be the next best step.


